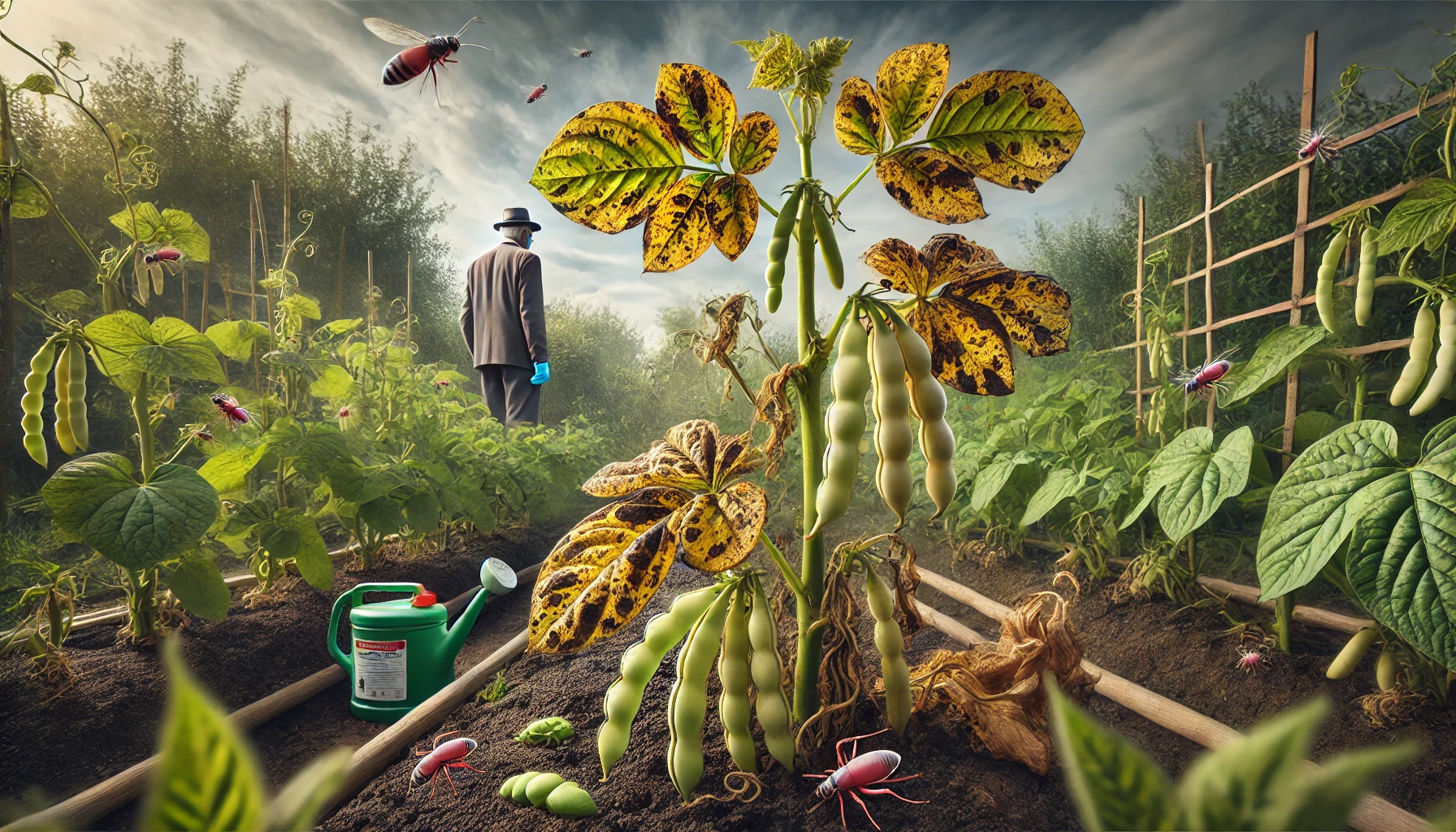
Kidney beans, like many other crops, are susceptible to a variety of diseases that can affect their growth and yield. Understanding these diseases, their symptoms, causes, cures, and prevention methods is crucial for maintaining healthy plants.
1. Anthracnose
- Symptoms of Anthracnose:
- Dark, sunken lesions on stems, leaves, and pods.
- Leaf spots with dark borders.
- Pod lesions often turn brown and spread rapidly.
- Cause of Anthracnose:
- Caused by the fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum.
- Spread through infected seeds, plant debris, and splashing water.
- Cure for Anthracnose:
- Natural: Remove and destroy infected plant debris.
- Organic: Apply neem oil or copper-based fungicides.
- Chemical: Use fungicides containing chlorothalonil or mancozeb.
- Prevention from Anthracnose:
- Use certified disease-free seeds.
- Practice crop rotation and avoid planting beans in the same location each year.
- Ensure good air circulation around plants by spacing them properly.
2. Root Rot of Kidney Bean
- Symptoms of Root Rot:
- Yellowing and wilting of leaves.
- Stunted growth and poor plant vigor.
- Roots appear dark, mushy, and decayed.
- Cause of Root Rot:
- Caused by various soil-borne fungi, including Rhizoctonia, Fusarium, and Pythium species.
- Poor drainage and overly wet soil conditions favor the disease.
- Cure for Root Rot:
- Natural: Improve soil drainage by adding organic matter like compost.
- Organic: Apply beneficial mycorrhizal fungi to enhance soil health.
- Chemical: Use soil fungicides like metalaxyl or Root Supplement products.
- Prevention from Root Rot:
- Avoid overwatering and ensure proper drainage.
- Use well-draining soil and raised beds.
- Rotate crops and avoid planting beans in the same soil consecutively.
3. Bean Mosaic Virus
- Symptoms of Mosaic Virus:
- Mottled or mosaic-like patterns on leaves.
- Distorted or curled leaves.
- Stunted growth and reduced pod production.
- Cause of Mosaic Virus:
- Caused by various viruses, including Bean common mosaic virus (BCMV) and Bean yellow mosaic virus (BYMV).
- Spread by aphids and through infected seeds.
- Cure for Mosaic Virus:
- Natural: Remove and destroy infected plants to prevent the spread.
- Organic: Use insecticidal soap to control aphid populations.
- Chemical: Apply insecticides to reduce aphid vectors.
- Prevention from Mosaic Virus:
- Plant virus-resistant bean varieties.
- Control aphid populations through natural predators or insecticides.
- Use certified virus-free seeds.
4. Bacterial Blight of Kidney Bean
- Symptoms of Bacterial Blight:
- Water-soaked spots on leaves that turn brown and necrotic.
- Pods may develop similar spots and become distorted.
- Yellowing and wilting of leaves.
- Cause of Bacterial Blight:
- Caused by bacteria Xanthomonas campestris (common blight) and Pseudomonas syringae (halo blight).
- Spread through infected seeds, plant debris, and splashing water.
- Cure for Bacterial Blight:
- Natural: Remove and destroy infected plant parts.
- Organic: Apply copper-based bactericides.
- Chemical: Use bactericides containing streptomycin or copper compounds.
- Prevention from Bacterial Blight:
- Use certified disease-free seeds.
- Avoid overhead watering to reduce leaf wetness.
- Practice crop rotation and sanitation by removing plant debris.
General Prevention Tips for Kidney Bean Diseases
- Choose Disease-Resistant Varieties: Select bean varieties that are bred for resistance to common diseases.
- Proper Spacing: Ensure adequate spacing between plants to improve air circulation and reduce humidity around the foliage.
- Good Watering Practices: Water plants at the base to avoid wetting the leaves and water early in the day to allow foliage to dry.
- Crop Rotation: Rotate crops each year to prevent the buildup of soil-borne pathogens.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy any diseased plant material and practice good garden hygiene.
By understanding the symptoms, causes, cures, and prevention methods for common kidney bean diseases, gardeners can effectively manage their crops and ensure healthy, productive plants.